BCAA 2:1:1
$29.95 – $49.95Price range: $29.95 through $49.95
Branch Chain Amino Acids (BCAA) is one of the ‘must take’ supplements for building muscle. The three proteinogenic BCAAs are among the nine essential amino acids for humans, accounting for 35% of the essential amino acids in muscle proteins and 40% of the preformed amino acids required by mammals1. Among the proteinogenic amino acids, there are three BCAAs: leucine, isoleucine and valine. It is therefore hardly a surprise to hear that the BCAA’s are vital for optimal muscle growth, endurance and the reduction in muscle soreness.
Provided in the most efficient manner of the 2:1:1 ratios, Branched Chain Amino Acids or BCAA’s for short are essential and foundation amino acids that are used prior to or during exercise to help buffer catabolic processes as well as providing the tools to further assist with anabolic growth and recovery. Leucine, one of the most popular of the 9 essential amino acids required by the body that it cannot synthesize itself, stimulates the mTOR signalling pathway which corresponds to the greater effects of Protein synthesis, insulin sensitivity and growth factors. BCAA’s also help to reduce the muscle soreness and damage that occurs after intense exercise
BCAA – FOR BOOSTING MUSCLE GROWTH AND PERFORMANCE
Branch Chain Amino Acids (BCAA) is one of the ‘must take’ supplements for building muscle. The three proteinogenic BCAAs are among the nine essential amino acids for humans, accounting for 35% of the essential amino acids in muscle proteins and 40% of the preformed amino acids required by mammals1. Among the proteinogenic amino acids, there are three BCAAs: leucine, isoleucine and valine. It is therefore hardly a surprise to hear that the BCAA’s are vital for optimal muscle growth, endurance and the reduction in muscle soreness.
Leucine for mTORc muscle growth.
The anabolic potential of leucine has been attributed to its capacity to stimulate translation initiation both dependently and independently of the mTORc signalling pathway. Interestingly, aging has been associated with impairment of nutrient-sensing signalling pathways. However, studies show that the postprandial phosphorylation of mTORc, and its downstream effector p70S6K, was more pronounced following long term leucine supplementation2. In addition to its effects on muscle protein synthesis, there is some evidence suggesting that leucine augments glucose-induced insulin secretion. In animal models, chronic leucine supplementation improved insulin sensitivity despite the consumption of a high-fat diet3. As we age, it becomes for difficult for us to maintain and gain muscle mass. Leucine supplementation increases the potential for muscle protein synthesis in older adults and may make an otherwise insufficient or marginal quantity of meal-derived protein more biologically available for muscle tissue growth and repair.4
The BCAA and the benefits during training
It is well documented that exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD) decreases muscle function and causes soreness and discomfort. We have all been there! BCAA supplementation has been shown to increase protein synthesis and decrease muscle protein breakdown, however, the effects of BCAAs on recovery from damaging resistance training needed to be clarified. Therefore, a study5 was conducted to examine the effects of a BCAA supplementation on markers of muscle damage elicited via a sport specific bout of damaging exercise in trained volunteers.
How the study was conducted.
Twelve males (mean ± SD age, 23 ± 2 y; stature, 178.3 ± 3.6 cm and body mass, 79.6 ± 8.4 kg) were randomly assigned to a BCAA supplement (n = 6) or placebo (n = 6) group. The damaging exercise consisted of 100 consecutive drop-jumps. Creatine kinase (CK), maximal voluntary contraction (MVC), muscle soreness (DOMS), vertical jump (VJ), thigh circumference (TC) and calf circumference (CC) were measured as markers of muscle damage. All variables were measured immediately before the damaging exercise and at 24, 48, 72 and 96 h post-exercise.
What happened?
There were significant group effects showing a reduction in CK efflux and muscle soreness in the BCAA group compared to the placebo (P<0.05). Furthermore, the recovery of MVC was greater in the BCAA group (P<0.05). The VJ, TC and CC were not different between groups.
What does this mean for you?
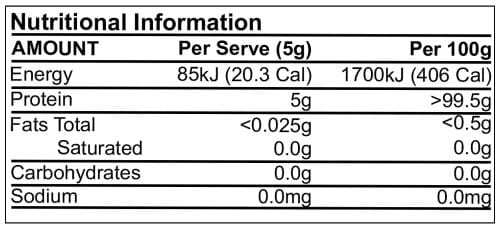
BCAA administered before and following damaging resistance exercise reduces indices of muscle damage and accelerates recovery in resistance-trained males. It seems likely that BCAA provided greater bioavailability of substrate to improve protein synthesis and thereby the extent of secondary muscle damage associated with strenuous resistance exercise. The dose used in this study was 10g of BCAA.
BCAA Summary
Supplementing BCAAs prevents a serum decline in BCAAs, which occurs during exercise. A serum decline would normally cause a tryptophan influx into the brain, followed by serotonin production, which causes fatigue. BCAA’s also help to reduce the muscle soreness and damage that occurs after intense exercise. BCAA also boost muscle growth via numerous growth pathways. Thus consuming a standard dose of BCAAs before and after exercise is virtually essential for optimal muscle growth and performance. If you exercise lasts for longer than one hour, consider pausing for a BCAA drink during your workout also.
Why should I take the ATP Science BCAA’s?
The starting material of ATP Science BCAA’s is glucose from non GMO corn. (Many materials on the market are produced from genetically modified corn).
Other unique benefits include:
Uses sunflower lecithin (instead of soy lecithin) for instantiation
Confirmed ratios (2:1:1) of Leucine, Isoleucine and Valine
Allergen, pesticide, heavy metal and microbial tested for compliance
Approved material manufacturer that will allow audits of their factory
Naturally fermented (naturally produced)
HPLC verified guaranteeing fully efficacious material and no contaminants or adulteration
High bioavailability
Vegan
Gluten free
GMO free
Sugar free
| Size | |
|---|---|
| Flavour |
Be the first to review “BCAA 2:1:1” Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a review.
Related products
Amino Acids
Body Building
Body Building
Body Building
Amino Acids
Body Building
Body Building
Meal Bags














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.